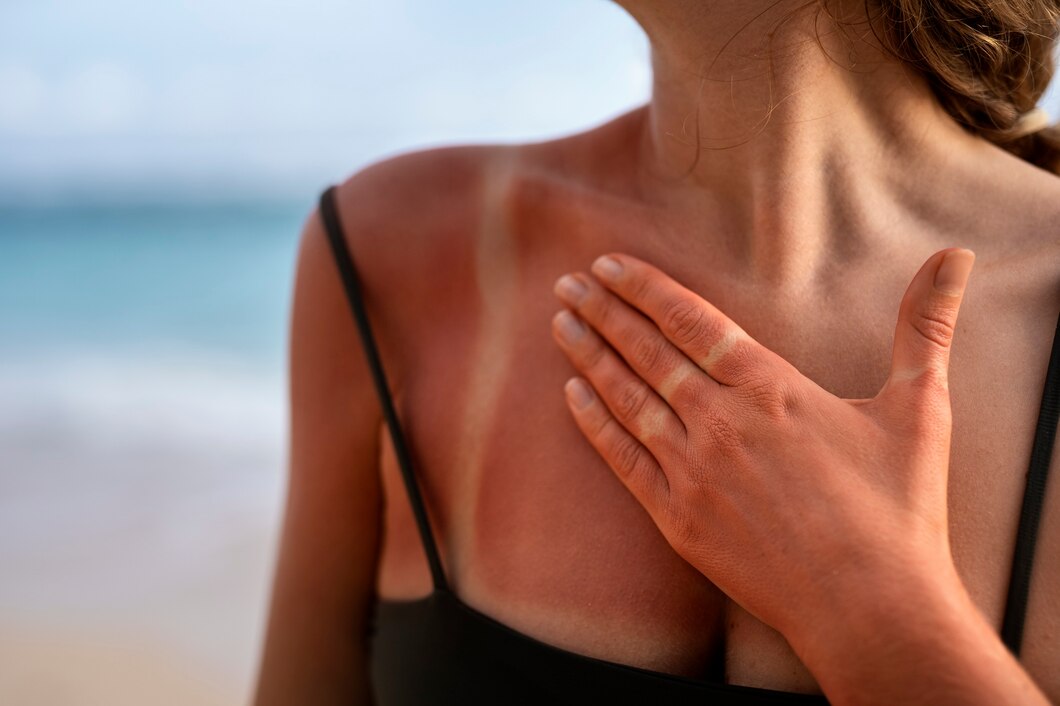
Sunburn is a common consequence of overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. While it may seem like a temporary discomfort, the effects of sunburn can have lasting implications on our skin health. Let’s delve into the causes and effects of sunburn to better comprehend this familiar but often underestimated condition.
Causes of Sunburn:
Sunburn occurs when the skin is exposed to excessive UV radiation, primarily from the sun. UV radiation is classified into three types: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, contributing to premature aging, while UVB rays are responsible for sunburn. UVC rays are mostly absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and don’t reach the surface.
When the skin absorbs UVB rays, it triggers a series of reactions that lead to damage. Melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, provides some natural protection by absorbing UV radiation. However, when the intensity of UV exposure exceeds the skin’s defense mechanisms, sunburn occurs.
Effects of Sunburn:
- Redness and Inflammation: The immediate aftermath of sunburn is often visible redness and inflammation. This is a result of blood vessels dilating in an attempt to repair the damaged tissue.
- Pain and Discomfort: Sunburned skin is sensitive and painful. The nerve endings in the skin become irritated, causing discomfort and tenderness.
- Peeling and Itching: As the skin tries to heal, it may peel. Itching can accompany this peeling phase, tempting individuals to scratch, which can exacerbate the damage.
- Dehydration: Sunburn can lead to fluid loss from the body, contributing to dehydration. It is crucial to stay well-hydrated, especially during the recovery period.
- Long-term Damage: Repeated sunburns can result in long-term damage, accelerating skin aging and increasing the risk of skin cancers, including melanoma.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Sunscreen: Regularly apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF to protect against both UVA and UVB rays.
- Protective Clothing: Wear protective clothing, including hats and sunglasses, to minimize direct sun exposure.
- Seek Shade: Limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours when UV radiation is strongest (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and aid in the healing process.
- Cooling Measures: Apply cool compresses, take cool baths, or use aloe vera gel to soothe sunburned skin.
Understanding the causes and effects of sunburn is essential for adopting preventive measures and promoting skin health. By respecting the sun’s power and taking proactive steps to protect our skin, we can enjoy the outdoors safely and reduce the risk of long-term damage.