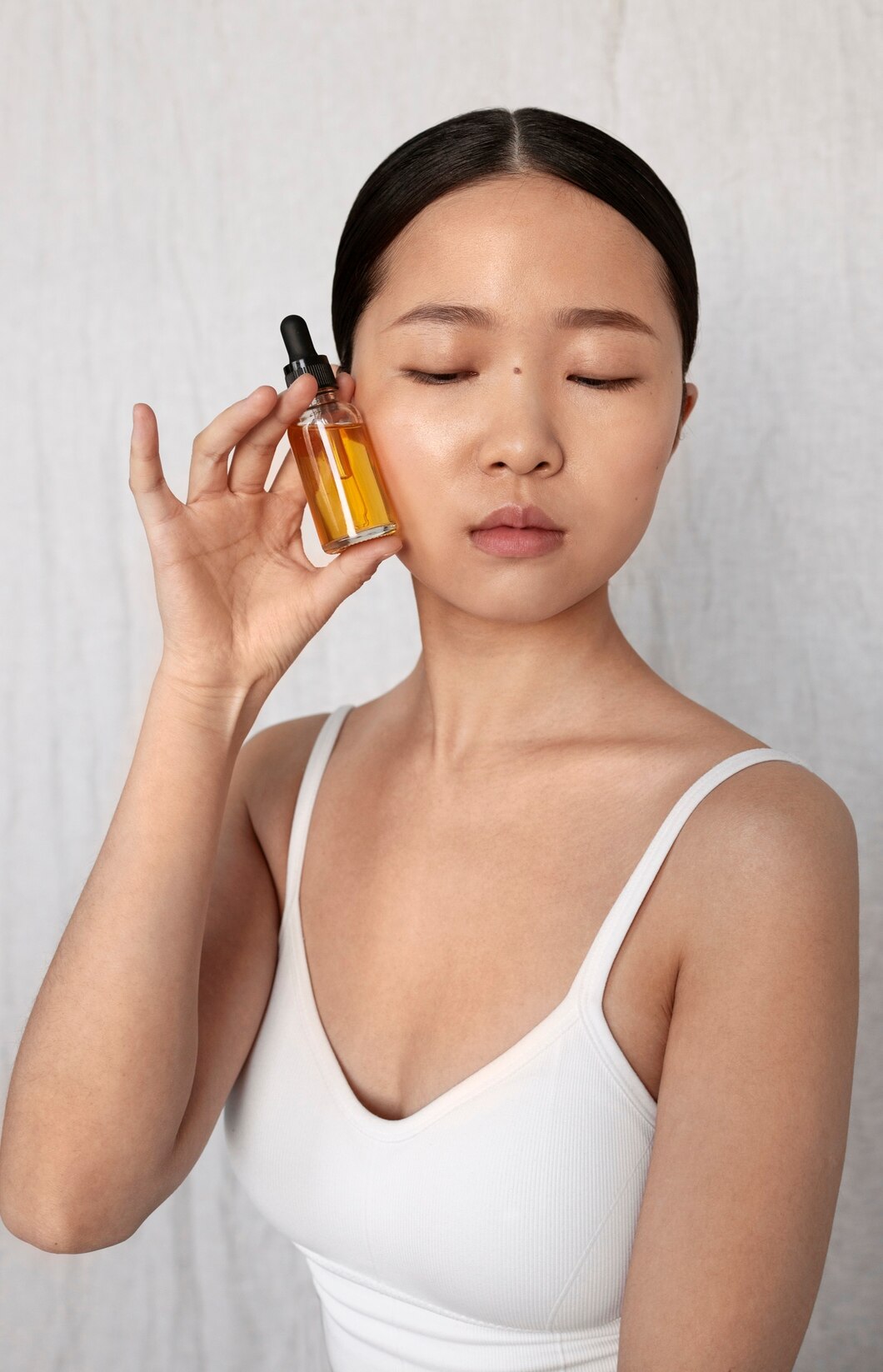
In the ever-evolving world of skincare, serums have emerged as potent players, promising targeted treatments for a variety of skin concerns. Their rise in popularity is backed by science, with formulations designed to deliver concentrated active ingredients directly into the skin. Understanding the science behind serums can help you make informed choices for achieving radiant skin.
What Are Serums?
Serums are lightweight, fast-absorbing liquids that contain a high concentration of active ingredients. Unlike moisturizers, which are primarily designed to hydrate and protect the skin, serums are formulated to address specific skin issues such as wrinkles, dark spots, and acne. Their smaller molecular size allows them to penetrate deeper into the skin, delivering active ingredients more effectively.
Key Ingredients in Serums and Their Benefits
Hyaluronic Acid
- Function: Hydration
- Benefit: Hyaluronic acid is a powerful humectant that attracts and retains moisture in the skin. It can hold up to 1,000 times its weight in water, providing deep hydration and plumping the skin to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Vitamin C
- Function: Antioxidant and Brightening
- Benefit: Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps protect the skin from environmental damage caused by free radicals. It also aids in collagen production and brightens the complexion, reducing the appearance of dark spots and uneven skin tone.
Retinol (Vitamin A)
- Function: Anti-Aging
- Benefit: Retinol accelerates cell turnover and stimulates collagen production, helping to reduce fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation. It can also improve skin texture and tone.
Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)
- Function: Anti-Inflammatory and Barrier Support
- Benefit: Niacinamide helps to reduce inflammation, redness, and blotchiness. It strengthens the skin’s barrier, improves elasticity, and diminishes dullness.
Peptides
- Function: Collagen Boosting
- Benefit: Peptides are short chains of amino acids that help build proteins in the skin, such as collagen and elastin. They help to firm and smooth the skin, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)
- Function: Exfoliation
- Benefit: AHAs, such as glycolic acid and lactic acid, exfoliate the skin by removing dead skin cells. This promotes a smoother, brighter complexion and can improve the effectiveness of other skincare products.
How to Use Serums Effectively
To maximize the benefits of serums, follow these steps:
- Cleanse: Start with a clean face to ensure that the serum can penetrate effectively.
- Apply Toner (Optional): If you use a toner, apply it before the serum to prepare your skin.
- Apply Serum: Use a few drops of serum and gently pat it into your skin. Avoid rubbing, as this can irritate the skin.
- Moisturize: After the serum has absorbed, apply your regular moisturizer to lock in the benefits.
- Sunscreen (Morning Routine): If using the serum in the morning, follow up with sunscreen to protect your skin from UV damage.
Choosing the Right Serum for Your Skin Type
- Dry Skin: Look for serums with hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and ceramides to boost hydration.
- Oily/Acne-Prone Skin: Opt for serums containing salicylic acid, niacinamide, and retinol to regulate oil production and treat acne.
- Sensitive Skin: Choose gentle formulations with ingredients like niacinamide and peptides to reduce irritation and strengthen the skin barrier.
- Aging Skin: Serums with retinol, peptides, and vitamin C can help address signs of aging such as wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots.
Serums are a powerhouse in the skincare world, offering targeted treatments for a variety of skin concerns. By understanding the science behind their ingredients and how to use them effectively, you can harness their full potential to achieve radiant, healthy skin. Whether you’re looking to hydrate, brighten, or combat signs of aging, there’s a serum out there tailored to meet your needs.