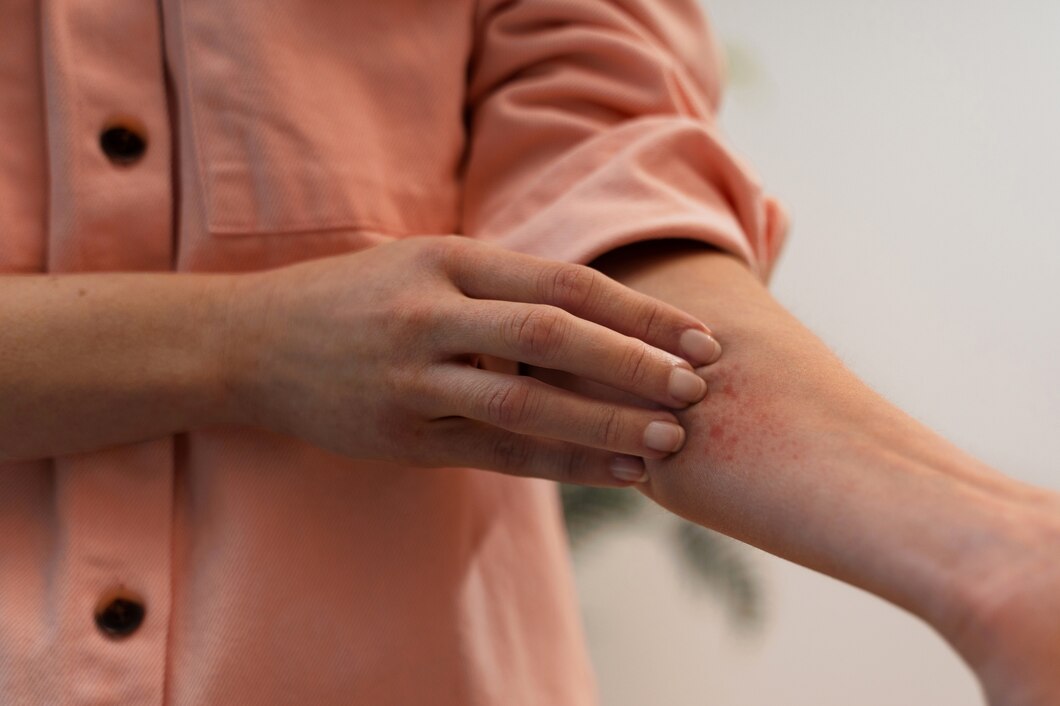
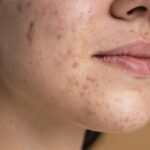
Eczema, a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation and itching, can be influenced by various factors, including diet. While not a one-size-fits-all solution, adjusting your eating habits can sometimes make a notable difference in managing eczema symptoms. Let’s explore the impact of diet on eczema and identify foods to include and avoid for healthier skin.
Foods to Include:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
- Found in fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce eczema symptoms.
Probiotics:
- Incorporate yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and other fermented foods rich in probiotics. These beneficial bacteria support gut health, potentially influencing the immune system’s response to inflammation.
Antioxidant-Rich Fruits and Vegetables:
- Colorful fruits and vegetables like berries, spinach, kale, and sweet potatoes are packed with antioxidants, which can help combat oxidative stress associated with eczema.
Quercetin-Containing Foods:
- Quercetin, found in apples, onions, and broccoli, has anti-inflammatory and antihistamine properties, potentially assisting in managing eczema-related inflammation.
Hydration:
- Water plays a crucial role in maintaining skin hydration. Staying well-hydrated supports the skin barrier function and may alleviate dryness associated with eczema.
Foods to Avoid:
Common Allergens:
- Identify and eliminate common food allergens like dairy, eggs, nuts, and shellfish. These can trigger allergic reactions in some individuals with eczema.
Processed Foods:
- Highly processed foods often contain additives and preservatives that may exacerbate inflammation. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
Sugary Treats:
- Excessive sugar consumption can contribute to inflammation. Limiting intake of sugary treats, sodas, and processed sweets may help manage eczema symptoms.
Gluten:
- Some individuals with eczema may be sensitive to gluten. Experiment with a gluten-free diet to see if it positively impacts your skin condition.
Nightshade Vegetables:
- For some people, nightshade vegetables like tomatoes, eggplants, and peppers can trigger eczema flare-ups. Monitor your intake and observe any correlations.
Citrus Fruits:
- Citrus fruits are acidic and may irritate the skin in some cases. Consider reducing or eliminating citrus fruits if you notice a connection with eczema symptoms.
Dietary Tips for Eczema Management:
Keep a Food Diary:
- Track your food intake and note any changes in eczema symptoms. This can help identify specific trigger foods.
Consult a Healthcare Professional:
- Before making significant dietary changes, consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation.
Gradual Changes:
- Introduce dietary changes gradually. Abrupt shifts can make it challenging to pinpoint specific triggers.
Listen to Your Body:
- Pay attention to how your body responds to different foods. If you notice improvements or worsening of symptoms, adjust your diet accordingly.
While dietary adjustments may not be a universal cure for eczema, they can play a supportive role in managing symptoms. It’s essential to approach dietary changes with patience, observe how your body responds, and seek professional guidance for a tailored plan that suits your individual needs.