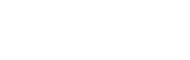Chemical peels have become a popular and effective skincare treatment, offering a transformative experience for those seeking to improve the appearance and texture of their skin. But what exactly happens during a chemical peel, and how do these treatments work to rejuvenate the skin? In this article, we will delve into the science behind chemical peels and explore the mechanisms that contribute to their skin-transforming effects.
Understanding Chemical Peels:
A chemical peel involves the application of a chemical solution to the skin, which causes controlled exfoliation and encourages the regeneration of new, healthier skin cells. The specific combination of chemicals used and the depth of penetration determine the type and intensity of the peel.
The Three Main Types of Chemical Peels:
- Superficial Peels:
Chemicals Used: Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) such as glycolic acid.
Mechanism: These peels target the outermost layer of the skin (epidermis), providing a mild exfoliation. They are suitable for addressing minor skin concerns, improving texture, and enhancing overall skin brightness. - Medium Peels:
Chemicals Used: Trichloroacetic acid (TCA).
Mechanism: Penetrating the epidermis and reaching the upper part of the middle skin layer (dermis), medium peels address more significant skin issues. They are effective in treating sun damage, fine lines, and pigment irregularities. - Deep Peels:
Chemicals Used: Phenol.
Mechanism: Penetrating deeper into the dermis, deep peels offer substantial skin rejuvenation. They are capable of addressing more severe issues such as deep wrinkles, scars, and precancerous growths. However, deep peels often require a longer recovery period.
The Science in Action:
- Exfoliation and Cell Turnover:
The chemical solution applied during a peel induces exfoliation by breaking down the bonds between old, damaged skin cells. This process stimulates cell turnover, promoting the emergence of new, healthy skin cells. - Collagen Stimulation:
Chemical peels trigger the production of collagen, a crucial protein responsible for skin firmness and elasticity. Increased collagen production contributes to a smoother, more youthful appearance. - Pigmentation Regulation:
Chemical peels can regulate melanin production, addressing issues like hyperpigmentation, sunspots, and uneven skin tone. By promoting even pigment distribution, the skin achieves a more uniform complexion. - Stimulation of Hydration:
Peels can enhance the skin’s ability to retain moisture by promoting the synthesis of hyaluronic acid. Improved hydration levels contribute to a plumper and more supple complexion. - Addressing Acne and Scarring:
Chemical peels are effective in treating acne and reducing the appearance of acne scars. They exfoliate the skin’s surface, unclog pores, and encourage the healing of blemishes.
Post-Peel Care:
Understanding the science behind chemical peels extends to recognizing the importance of post-peel care. After the exfoliation process, the skin is more sensitive and susceptible to damage from UV rays. Sun protection, hydration, and following post-peel care instructions provided by skincare professionals are essential for optimal results and recovery.
The science behind chemical peels underscores their ability to transform the skin by promoting exfoliation, collagen production, and targeted treatment of various skin concerns. Whether opting for a superficial, medium, or deep peel, individuals seeking skin rejuvenation can benefit from understanding how these treatments work at a cellular level. As with any skincare procedure, consulting with a qualified skincare professional ensures a personalized approach that aligns with individual skin needs and goals.