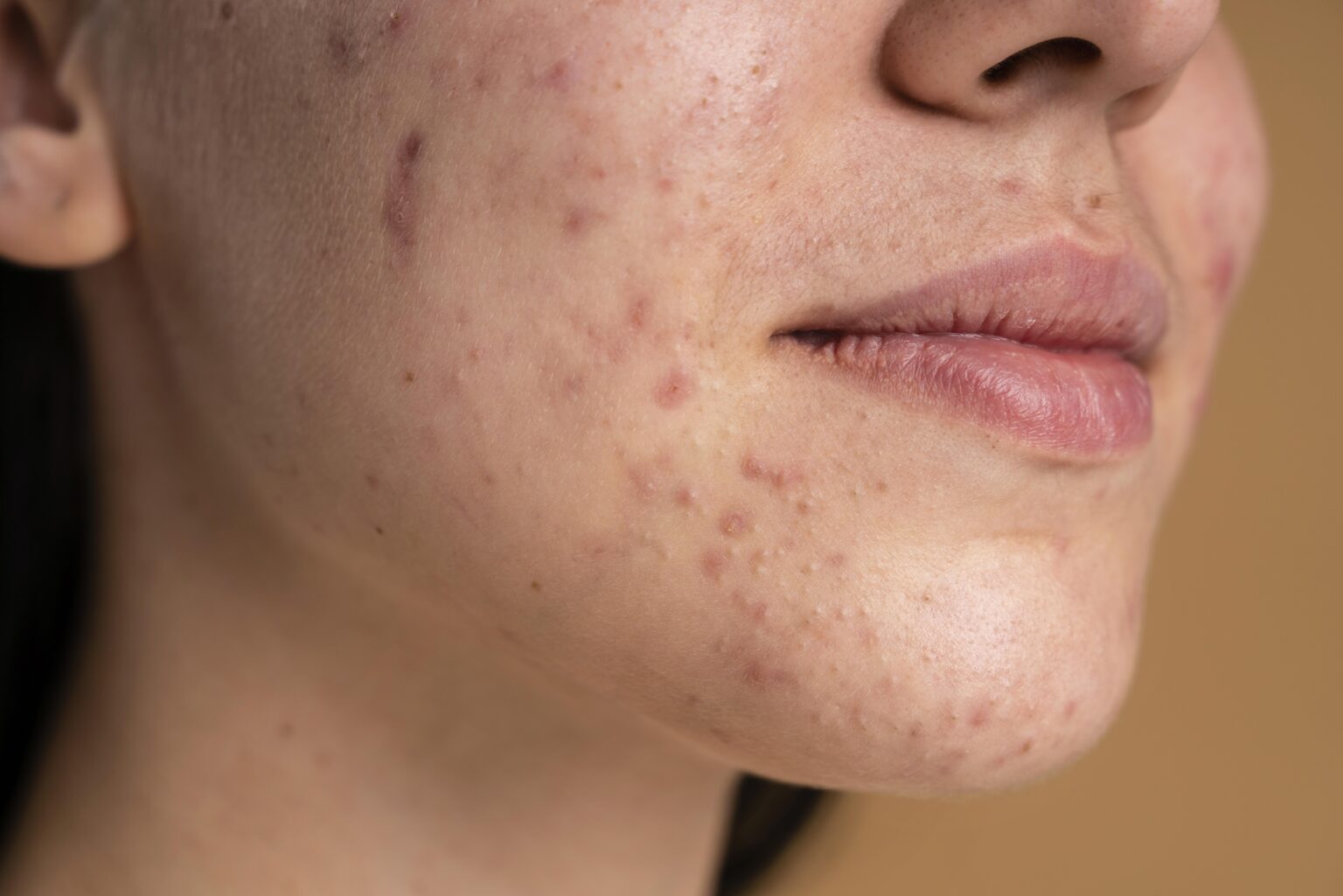
Acne is a common skin condition that can affect individuals of all ages, but for many, hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in the development of persistent breakouts. Hormonal acne, often experienced during adolescence, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, is a result of fluctuating hormone levels that influence the skin’s oil production. In this article, we will delve into the relationship between hormonal fluctuations and acne, offering insights into managing hormonal breakouts.
The Role of Hormones in Acne Formation
- Androgens and Sebum Production:
Hormones known as androgens, particularly testosterone, stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce sebum, an oily substance that can clog pores when overproduced. - Increased Sebum and Acne Formation:
Excess sebum mixes with dead skin cells, creating a favorable environment for the proliferation of acne-causing bacteria. This can lead to inflammation, redness, and the formation of various types of acne lesions.
Hormonal Fluctuations and Acne Triggers
- Adolescence:
The surge of androgens during puberty is a common trigger for hormonal acne. Increased sebum production can result in blackheads, whiteheads, and inflammatory acne lesions. - Menstrual Cycle:
Many women experience hormonal acne during the menstrual cycle, typically around the time of ovulation and just before menstruation. Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can influence sebum production. - Pregnancy:
Pregnancy induces hormonal changes, and some women may experience acne as a result. However, for others, pregnancy hormones can have a positive effect on the skin, leading to an improvement in acne. - Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
Hormonal imbalances associated with conditions like PCOS can contribute to persistent hormonal acne. Elevated androgen levels are common in PCOS, leading to increased sebum production and acne.
Managing Hormonal Breakouts: Insights and Strategies
- Consultation with a Dermatologist:
Seeking guidance from a dermatologist is crucial for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. Dermatologists can identify the specific factors contributing to hormonal acne and recommend targeted interventions. - Hormonal Birth Control:
For women experiencing hormonal acne related to the menstrual cycle, hormonal birth control methods like oral contraceptives can help regulate hormone levels and reduce acne severity. - Topical Retinoids:
Dermatologist-prescribed topical retinoids, such as tretinoin, can help regulate skin cell turnover, preventing the clogging of pores and reducing acne lesions. - Anti-Androgen Medications:
In cases of severe hormonal acne, anti-androgen medications may be prescribed to regulate androgen levels and subsequently reduce sebum production. - Lifestyle Modifications:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can complement medical treatments. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress through relaxation techniques, and ensuring proper sleep. - Gentle Skincare Routine:
Using a gentle skincare routine helps manage acne without causing additional irritation. Non-comedogenic products and mild cleansers can support overall skin health.
Understanding the intricate relationship between hormonal fluctuations and acne is essential for effective management. While hormonal acne can be challenging, numerous treatment options and lifestyle modifications are available to help individuals achieve clearer, healthier skin. Seeking professional advice and adopting a holistic approach to skincare can empower individuals to navigate hormonal breakouts successfully and regain confidence in their skin health.